Abstract
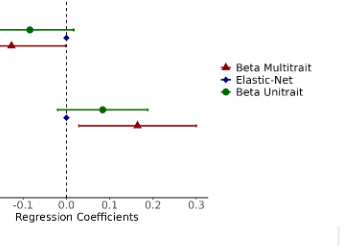
The ability to assess one's own cognitive processes across different domains is known as metacognition. Although it has been hypothesized that people with certain personality disorders have trouble understanding their own mental states, its relationship with metacognition remains unclear. In an online study, participants from the general population completed the Personality Inventory Disorders 5 (PID-5) for DSM-5 after completing a dot-density perceptual task. Participants reported their confidence levels on each trial. Using a bias-free metacognitive measure, we conducted several regression models to explore the relationship between metacognitive sensitivity and confidence with dysfunctional personality traits. We found evidence that Grandiosity, Perceptual Dysregulation, Restricted Affectivity, Separation Insecurity, Hostility, Impulsivity and Submissiveness dysfunctional personality facets are associated with confidence level. Moreover, Anxiousness and Emotional Lability showed connections with metacognitive sensitivity. These results support the idea of a potential link between metacognition and mental health in the context of a transdiagnostic framework for personality disorders.
Preprint here